AI Business Solutions: Transforming Enterprises with Artificial Intelligence
- Carlos Martinez
- Jul 9, 2025
- 8 min read
The global enterprise artificial intelligence market is projected to grow from $1.51 billion in 2024 to $14.44 billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.6%, according to Business Research Insights. This growth reflects more investment and adoption, as companies integrate AI into their existing processes and systems.
AI business solutions refer to technologies and services that apply machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and other AI capabilities to everyday operations.
These solutions help businesses move faster, make better decisions, and unlock new value from their data.
TL;DR: Most enterprises already have the data to improve efficiency and revenue -they just don’t use it well. Here’s how you can evaluate and leverage AI solutions in your business without the noise.
How Can AI Be Used for Business?
AI now supports many core business activities. Companies apply it to automate routine tasks, improve decision-making, and strengthen security. For example, AI systems can process large volumes of data to predict demand trends, recommend products, or detect fraud.
In operations, AI helps with automating workflows like data entry, scheduling, and report generation. In sales and marketing, it powers personalized recommendations, lead scoring, and content optimization.
AI tools also play a growing role in cybersecurity by monitoring network activity and identifying potential threats in real time.
Area | Use Cases |
Customer Experience | Personalized recommendations, Chatbots, Personalized marketing |
Business Operations | Automation, Predictive analytics, Supply chain optimization, Fraud detection |
Sales & Marketing | Lead generation and nurturing, Content creation, SEO optimization |
Security | Threat detection and response, Access control, Cybersecurity risk assessment |
Business Development | Market research, Business plan generation, Product design & dev |
While applications differ by industry, the primary goal remains the same: to utilize data and automation to enhance accuracy, minimize manual effort, and achieve better outcomes.
Industry Use Cases
AI adoption varies across industries, depending on the specific challenges and operational goals. Here are examples of how different sectors are putting AI to work in measurable ways:
1. Retail
Retailers often deal with unpredictable demand and complex supply chains. Predictive analytics helps forecast sales trends and optimize inventory.
For example, Boll & Branch built an AI-driven ERP integration that connects order data across systems, enabling automated inventory tracking and checkout optimization. This kind of approach can improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
Importantly, 87% of retail leaders report that AI has had a positive impact on their revenue.
2. Manufacturing
AI supports predictive maintenance, quality control, and production planning. Some manufacturers are also embedding AI directly into products.
Automaker Rivian integrates AI prediction technology in its R1T and R1S vehicles and is exploring additional AI and generative AI capabilities in future models.
3. Financial Services
Real-time fraud detection systems use AI to monitor transactions and flag suspicious activity. American Express, for example, relies on AI to analyze over $1 trillion in transactions each year, reducing fraud risk and supporting compliance efforts.
4. Healthcare
AI improves diagnostic accuracy and patient engagement. The University of Rochester Medical Center distributed handheld imaging probes powered by AI to medical staff, speeding up diagnosis of conditions like cholecystitis and improving patient access to care.
They plan to triple the number of devices in use by 2026.
5. Logistics
AI-powered route planning and dynamic pricing help companies manage last-mile delivery and adapt to fluctuating demand. Predictive models optimize fleet utilization and improve delivery times.
6. Energy
AI helps monitor infrastructure and reduce emissions. Duke Energy worked with Microsoft to build an AI solution that detects methane leaks more accurately than manual estimates, supporting their net-zero goals.

7. Agriculture
AI models guide decisions on planting, irrigation, and sustainability. McKinsey research notes that analytical AI and generative AI can add significant value across functions such as R&D, agronomy, and operations.
8. Telecommunications
Predictive maintenance tools help reduce network outages, while AI-driven retention systems personalize offers to limit customer churn.
9. Professional Services
Natural language processing automates document review and extraction, saving time and reducing manual errors in tasks like contract analysis.
What Are AI-Powered Business Solutions?
AI-powered business solutions integrate intelligent capabilities into core processes to improve accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
They address specific operational problems rather than adding technology for its own sake. For example:
AI Automation Services
Automation is often the most accessible entry point. It targets high-volume, repetitive tasks and supports more consistent output.
According to McKinsey, existing technologies could automate up to 45% of current work activities. Common examples include:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
Software bots perform routine actions such as data entry, invoice processing, and transaction handling. RPA tools work with existing systems without major changes.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP):
AI systems extract and organize information from unstructured documents like contracts and forms, reducing manual review time.
Conversational AI:
Chatbots and virtual assistants respond to inquiries, assist with transactions, and escalate complex issues to human agents when needed.
Predictive Analytics:
Machine learning models forecast demand, identify potential risks, and support planning based on historical data patterns.
Computer Vision:
Image analysis tools detect defects, monitor assets, and support inventory management by processing visual inputs in real time.
AI Managed Services
Some organizations rely on managed services to deploy and maintain AI systems. Providers handle data pipelines, model development, monitoring, and updates under service agreements.
This approach can be useful for companies without large internal AI teams or infrastructure.
Cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer managed services that scale with usage and provide support without requiring dedicated in-house resources.
AI Center of Excellence (CoE)
An AI Center of Excellence helps coordinate projects, develop shared standards, and provide oversight across teams. A CoE typically includes technical specialists and business stakeholders who work together to set priorities, define practices, and share tools.
This structure supports consistent implementation and helps avoid duplication of effort across departments.
AI Technologies & Underlying Capabilities
1. Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms learn patterns from historical data to make predictions or classify information. They support use cases such as demand forecasting, fraud detection, and customer segmentation.
Models can be trained with labeled data (supervised learning), find patterns in unlabeled data (unsupervised learning), or optimize actions through trial and error (reinforcement learning).
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables software to interpret and generate human language. Applications include chatbots that handle customer queries, tools that extract information from contracts, and systems that analyze sentiment in customer feedback.
Modern NLP models handle context and nuance across multiple languages.
3. Computer Vision
Computer vision systems analyze images and video to detect objects, classify scenes, or identify defects. Common business uses range from quality inspection in manufacturing to medical imaging and inventory tracking in retail environments.
4. Reinforcement Learning
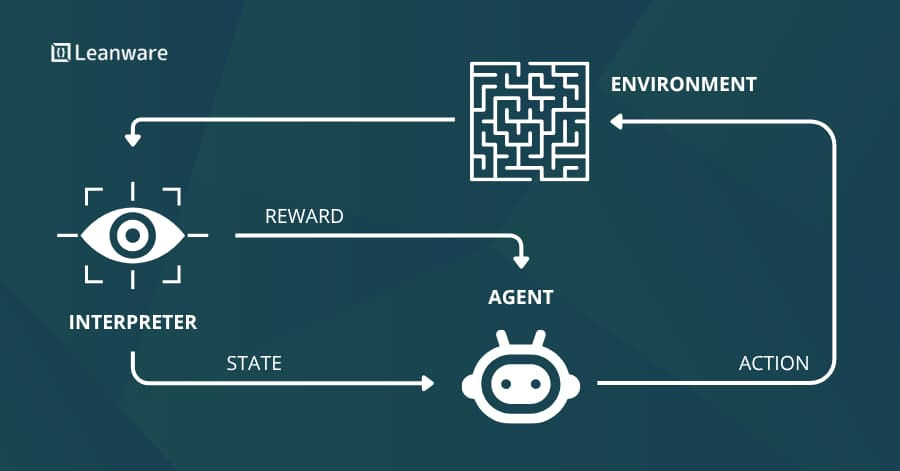
Reinforcement learning algorithms improve decision-making by testing different strategies and learning from outcomes. They are often applied in areas like dynamic pricing, resource scheduling, and recommendation systems.
How to Start Implementing AI in Your Business

It is a structured approach that connects technology to measurable business goals. Enterprises benefit most when they start small, validate results, and expand systematically.
1. Identify Priority Use Cases
Focus first on problems where AI can deliver clear value. Common examples include automating repetitive tasks, improving demand forecasting, detecting anomalies, or improving customer support.
Prioritize use cases that align with strategic goals and have accessible, reliable data.
2. Assess Data and Infrastructure Readiness
Evaluate whether you have the data quality, volume, and infrastructure needed to train and deploy AI models. Identify gaps in data pipelines, storage, and integration with existing systems like ERP or CRM platforms.
3. Develop a Pilot Project
Create a small-scale pilot to test the technology and measure impact. Define clear success criteria, such as error reduction, time savings, or improved forecast accuracy and set a realistic timeline for evaluation.
4. Build Internal Capability and Partnerships
Decide whether to develop AI capabilities in-house or work with external partners. Many enterprises combine both approaches: building core knowledge internally while engaging specialists for implementation and support.
Train teams on AI fundamentals to ensure alignment and adoption.
5. Plan for Scaling and Change Management
Once the pilot shows results, prepare to scale across the organization. Standardize processes, document lessons learned, and invest in tools that support broader adoption.
Develop a change management plan to address cultural and workflow adjustments.
Benefits & Business Impact of AI

AI creates measurable improvements across cost, revenue, risk, and innovation. For most enterprises, value comes not only from automating existing processes but also from enabling better decisions and faster experimentation.
According to McKinsey, generative AI alone has the potential to generate between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion in value annually across industries.
1. Operational Efficiency
AI improves efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors, and optimizing how resources are used.
Companies often see processing times shrink from hours to minutes and experience 15-25% cost savings in areas like data entry, scheduling, and supply chain operations.
2. Revenue Growth
Personalization engines and predictive analytics help increase sales conversions and improve customer retention.
By delivering more relevant recommendations and anticipating customer needs, businesses can grow revenue by 5–15% while enhancing customer loyalty.
3. Risk Reduction
AI strengthens compliance and risk management by spotting anomalies and detecting fraud in real time. Automated monitoring helps prevent losses and supports regulatory reporting with greater accuracy and less manual effort.
4. Faster Innovation
Machine learning models and analytics platforms make it easier to test ideas, adjust products, and launch new services based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Teams can iterate faster, supported by insights drawn from large volumes of data.
Getting Started
AI doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing commitment. You can start with focused projects that address clear problems and build momentum over time.
The most effective efforts often begin with a few use cases that deliver measurable results and create support across the business.
As you plan, look for areas where better data, faster decisions, or more efficient processes will make the biggest difference.
Build partnerships, prepare your teams, and set realistic expectations so you can move from experiments to practical outcomes.
You can also reach out if you’d like a perspective on your plans or need help mapping out where AI could make the most impact in your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of AI business solutions?
AI business solutions include automation services (RPA, chatbots), predictive analytics, computer vision systems, natural language processing applications, and AI-powered decision support systems.
These solutions address specific business challenges across functions like customer service, operations, marketing, and finance.
How much does it cost to implement AI in a business?
AI implementation costs vary widely depending on scope, complexity, and your existing systems. Pilot projects often start between $50,000 and $500,000, while large-scale deployments can reach several million dollars.
Cloud-based services can reduce upfront expenses by using subscription pricing. You can also contact an AI consulting partner to get a clearer view of budgets, timelines, and options for your specific situation.
How do we measure the ROI of AI initiatives?
ROI is typically measured by comparing pre- and post-implementation metrics tied to cost savings, revenue growth, or efficiency gains.
Common indicators include reduced processing time, lower error rates, improved forecast accuracy, or increased customer retention. It’s important to establish baselines early and track outcomes over time.
How long does it take to see results from AI implementations?
Simple AI applications like chatbots can show results within weeks, while complex machine learning projects may take 6-18 months to deliver measurable benefits. Success depends on data quality, organizational readiness, and project complexity.
What are the biggest challenges in AI adoption?
Common challenges include data quality issues, skill shortages, integration with existing systems, change management resistance, and unrealistic expectations.
Organizations succeed by starting with pilot projects, investing in training, and maintaining realistic timelines and expectations.





.webp)








